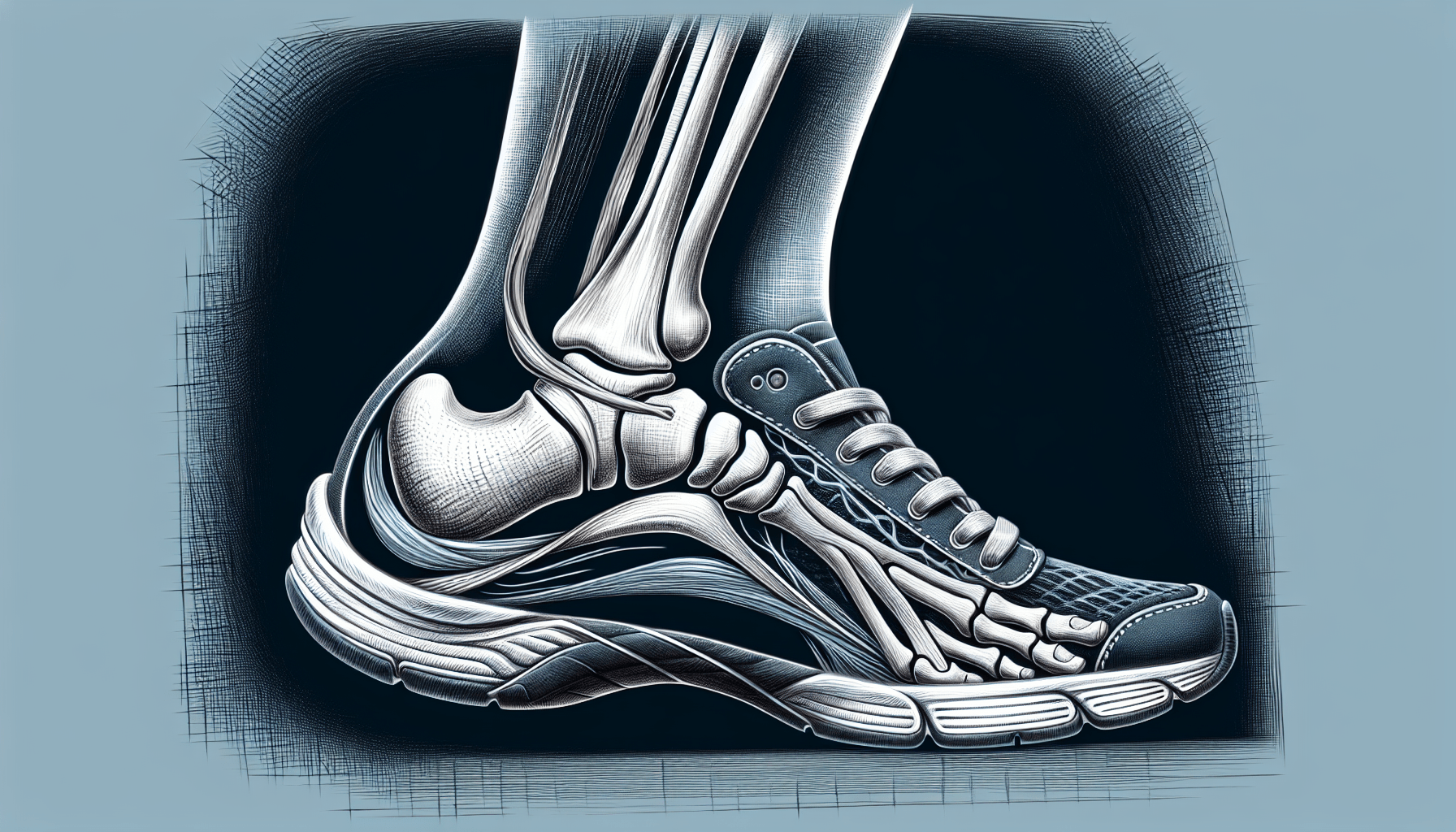
Plantar fasciitis, a condition that causes pain and inflammation in the sole of the foot, can be a frustrating and debilitating experience. Those who suffer from this condition often experience heel pain in the morning, discomfort after prolonged standing, and pain when extending their toes. The root causes of plantar fasciitis can vary, from inflammation and micro-tears in the plantar fascia to overuse, inadequate footwear, or obesity. To ensure proper recovery, it’s important to track the healing process and look out for signs of improvement such as reduced morning pain, increased range of motion, and diminished swelling. Treatment options range from home remedies and physical therapy to surgical interventions, while prevention strategies involve wearing supportive footwear, regular stretching and strengthening exercises, and maintaining a healthy weight. Taking care of foot health and addressing any concerns promptly is crucial for preventing plantar fasciitis and maintaining overall well-being.

This image is property of assets-global.website-files.com.
Understanding Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot condition that many people experience at some point in their lives. It is characterized by pain and inflammation in the sole of the foot, specifically in the plantar fascia. The plantar fascia is a thick band of tissue that connects the heel to the toes, and it plays an important role in supporting the arch of the foot.
Significance of Understanding Plantar Fasciitis
Understanding plantar fasciitis is crucial for several reasons. First and foremost, it allows individuals to recognize the symptoms and seek appropriate treatment in a timely manner. Early intervention can often lead to better outcomes and faster recovery. Additionally, understanding the causes and risk factors associated with plantar fasciitis can help individuals make lifestyle changes to prevent the condition from developing or recurring in the future.

This image is property of assets-global.website-files.com.
Causes of Plantar Fasciitis
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis. These include:
Overuse and Repetitive Activities
Engaging in activities that put excessive strain on the plantar fascia, such as running, jumping, or standing for long periods, can lead to inflammation and micro-tears in the tissue. Over time, this can result in plantar fasciitis.
Inadequate Footwear
Wearing shoes that do not provide proper support or cushioning can increase the risk of developing plantar fasciitis. Shoes that are worn out, have worn-out soles, or do not have adequate arch support can exacerbate the condition.
Obesity and Weight Gain
Excess weight can put additional pressure on the plantar fascia, leading to inflammation and pain. Individuals who are overweight or have recently gained weight may be more prone to developing plantar fasciitis.
Biomechanical Factors
Certain biomechanical issues, such as flat feet or high arches, can increase the risk of plantar fasciitis. These structural abnormalities can alter the way weight is distributed on the foot, putting added stress on the plantar fascia.
Age and Gender
Plantar fasciitis is more common in middle-aged individuals, typically between the ages of 40 and 60. It also tends to affect women more often than men, although the reasons behind this gender disparity are not fully understood.
Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis
Recognizing the common symptoms of plantar fasciitis is essential for prompt diagnosis and treatment. These symptoms may vary from person to person, but some of the most common ones include:
Heel Pain in the Morning
One of the hallmark symptoms of plantar fasciitis is experiencing intense heel pain immediately upon waking up in the morning. The pain is often described as a sharp or stabbing sensation and tends to decrease as the day goes on.
Pain after Extended Periods of Standing
People with plantar fasciitis often experience increased pain after standing or walking for an extended period. This can make it challenging to engage in activities that require prolonged periods of weight-bearing, such as running or standing at work.
Pain when Extending Toes
Another typical symptom of plantar fasciitis is experiencing pain when attempting to extend or curl the toes. This can be particularly noticeable when walking or engaging in activities that involve toe movement.
Occurrence and Frequency of Symptoms
The frequency and severity of symptoms can vary from person to person. Some individuals may only experience mild discomfort, while others may have significant pain that limits their daily activities. Symptoms can also come and go, with periods of flare-ups followed by periods of relative relief.

This image is property of assets-global.website-files.com.
Diagnosing Plantar Fasciitis
Diagnosing plantar fasciitis typically involves a combination of physical examination, a medical history assessment, and sometimes imaging and diagnostic tests.
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, a healthcare provider will assess the affected foot, looking for signs of tenderness, redness, or swelling. They may also evaluate the range of motion of the foot and ankle to determine any limitations.
Medical History Assessment
A healthcare provider will also ask about the individual’s symptoms, the duration and frequency of pain, and any factors that seem to worsen or alleviate the symptoms. They may inquire about the individual’s activity level, footwear, and any previous foot or leg injuries.
Imaging and Diagnostic Tests
In some cases, imaging studies such as X-rays or an MRI may be ordered to rule out other potential causes of foot pain or to assess the extent of the inflammation or damage to the plantar fascia. These tests can help confirm a diagnosis of plantar fasciitis and guide appropriate treatment.
Tracking the Healing Process
Monitoring the healing process is essential to ensure proper recovery from plantar fasciitis. It allows individuals and healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of the chosen treatment plan and make any necessary adjustments. Some signs of healing to look out for include:
Reduced Morning Pain
As the plantar fascia heals, individuals should notice a decrease in the intensity and duration of the morning heel pain. This is often one of the first signs that the treatment is working.
Decreased Pain during Activities
As the condition improves, individuals should experience reduced pain during activities that previously caused discomfort, such as walking, running, or standing for extended periods.
Improved Range of Motion
As the inflammation and tension in the plantar fascia subside, individuals may notice an improvement in their foot’s range of motion. This can make activities like stretching or bending the foot more comfortable and less restrictive.
Diminished Swelling and Inflammation
Swelling and inflammation are common symptoms of plantar fasciitis. Over time, with proper treatment and care, individuals should see a reduction in these symptoms.
Increased Pain Threshold
The pain threshold refers to the level at which an individual experiences pain. As plantar fasciitis heals, individuals may notice that they can tolerate more activity with less discomfort.
Less Discomfort in the Lower Body
Plantar fasciitis can cause discomfort that radiates beyond the foot and into the lower leg or calf. As the condition improves, individuals may experience less pain and discomfort in these areas.
Improved Strength and Stability
As the plantar fascia heals and the pain subsides, individuals can gradually regain strength and stability in the affected foot. This can make it easier to engage in physical activities without fear of re-injury or exacerbation of symptoms.
Monitoring the healing process often involves regular check-ins with a healthcare provider, who can assess progress, make recommendations, and provide additional treatments or interventions if needed.

This image is property of assets-global.website-files.com.
Home Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis
In addition to professional treatment, there are several home remedies that individuals can try to help alleviate symptoms and promote healing. These remedies include:
Rest and Ice
Resting the affected foot and applying ice to the area can help reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief. Ice can be applied for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
Orthotic Devices
Wearing orthotic devices, such as arch supports or shoe inserts, can help provide additional support and cushioning to the foot. These devices can help redistribute pressure and relieve strain on the plantar fascia.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Engaging in regular stretching and strengthening exercises can help improve flexibility, reduce tension in the plantar fascia, and promote healing. Examples of exercises that may be beneficial include calf stretches, toe curls, and towel scrunches.
Night Splints
Night splints are devices that help keep the foot in a neutral position during sleep. They can help prevent the plantar fascia from tightening and provide relief from morning heel pain.
Footwear Modifications
Wearing shoes that provide proper arch support, cushioning, and stability can help alleviate symptoms and support the healing process. Avoiding shoes with high heels or minimal support is important.
It is important to note that home remedies may provide temporary relief but should not replace professional medical advice or treatment. If symptoms persist or worsen, it is important to seek guidance from a healthcare provider.
Physical Therapy for Plantar Fasciitis
Physical therapy is often a key component of treatment for plantar fasciitis. It focuses on improving mobility, reducing pain, and strengthening the affected foot. Some common physical therapy techniques for plantar fasciitis include:
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
A physical therapist may prescribe specific exercises to stretch and strengthen the plantar fascia and surrounding muscles. These exercises are typically tailored to the individual’s needs and may involve activities like calf stretches, towel scrunches, or toe curls.
Massage and Manual Therapy
Massage and manual therapy techniques, such as deep tissue massage or myofascial release, may be used to help reduce tension in the plantar fascia, improve blood flow, and promote healing. These techniques can also help alleviate muscle knots and trigger points that may contribute to foot pain.
Ultrasound and Electrical Stimulation
Ultrasound therapy and electrical stimulation are commonly used modalities in physical therapy for plantar fasciitis. Ultrasound therapy uses high-frequency sound waves to promote tissue healing and reduce inflammation, while electrical stimulation can help improve muscle function and reduce pain.
Gait Analysis and Biomechanical Corrections
A physical therapist may perform a gait analysis to assess how an individual walks or runs and identify any abnormalities or imbalances that may contribute to plantar fasciitis. Based on the findings of the analysis, the therapist may recommend orthotic devices, shoe modifications, or other interventions to correct biomechanical issues and prevent further injury.
Physical therapy is typically tailored to the individual’s needs and goals. The frequency and duration of therapy sessions may vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s response to treatment.

This image is property of assets-global.website-files.com.
Surgical Interventions for Plantar Fasciitis
In severe cases of plantar fasciitis that do not respond to conservative treatments, surgery may be considered as a last resort. Surgical interventions for plantar fasciitis may involve:
Indications for Surgery
Surgery for plantar fasciitis is generally only considered when all other treatment options have been exhausted and symptoms continue to significantly impact an individual’s daily life. Severe pain, persistent symptoms despite conservative treatment, and functional limitations are some indications for surgery.
Common Procedures
The most common surgical procedure for plantar fasciitis is called a plantar fasciotomy. During this procedure, a surgeon makes small incisions in the plantar fascia to release tension and alleviate pressure on the affected area. In some cases, a partial or complete removal of the plantar fascia may be necessary.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery after surgical intervention for plantar fasciitis typically involves a period of immobilization, followed by a gradual return to weight-bearing activities. Physical therapy may be recommended to help regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the foot. The length of the recovery period can vary depending on the type of surgery performed and the individual’s response to treatment.
It is important to note that surgery is not always necessary for plantar fasciitis and is typically reserved for severe cases. Consultation with a healthcare provider or specialist is crucial to determine the most appropriate course of action.
Prevention of Plantar Fasciitis
While plantar fasciitis can be a challenging condition to manage, there are several preventive strategies that individuals can incorporate into their daily routines to reduce the risk of developing the condition. These strategies include:
Wearing Supportive Footwear
Investing in shoes that provide adequate arch support, cushioning, and stability is key in preventing plantar fasciitis. It is important to ensure that shoes fit properly and are appropriate for the specific activity or sport being performed.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Regularly engaging in stretching and strengthening exercises targeting the feet, calves, and ankles can help improve flexibility and reduce the risk of plantar fasciitis. Examples of exercises that may be beneficial include calf stretches, heel raises, and toe curls.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Excess weight can put additional strain on the plantar fascia, increasing the risk of inflammation and injury. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce the risk of developing plantar fasciitis.
Avoiding Overuse and Repetitive Activities
Engaging in activities that put excessive stress on the plantar fascia can increase the risk of developing plantar fasciitis. It is important to incorporate rest days into exercise routines and avoid overdoing high-impact activities.
Monitoring Foot Health
Monitoring foot health is an essential part of overall well-being and can help identify potential issues before they become serious problems. Regular foot exams, either self-examinations or conducted by a healthcare provider, can help identify any concerns or issues that may require medical attention.
Importance of Regular Foot Exams
Regular foot exams allow individuals to monitor the condition of their feet and identify any changes or abnormalities. They can help detect early signs of conditions like plantar fasciitis and enable prompt treatment.
Addressing Concerns and Seeking Medical Advice
If any concerns or issues are identified during a foot exam, it is important to seek medical advice. A healthcare provider or specialist can provide guidance, recommend appropriate treatments, and help prevent further complications.
Maintaining Overall Foot Health
In addition to regular foot exams, maintaining overall foot health is crucial in preventing conditions like plantar fasciitis. This includes practicing good foot hygiene, wearing appropriate footwear, and addressing any foot pain or discomfort promptly.
By incorporating these strategies into their daily routines, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent plantar fasciitis and ensure the health and well-being of their feet.
In conclusion, understanding plantar fasciitis is essential for recognizing the symptoms, seeking appropriate treatment, and taking preventive measures. By addressing the causes, symptoms, and diagnosis of plantar fasciitis, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and take steps to promote healing and prevent future issues. Whether through home remedies, physical therapy, or surgical interventions, there are several treatment options available to those affected by plantar fasciitis. By monitoring the healing process and practicing preventive measures, individuals can maintain overall foot health and well-being.